Gaussian Splatting
TitleWhat is Gaussian Splatting? (3DGS)
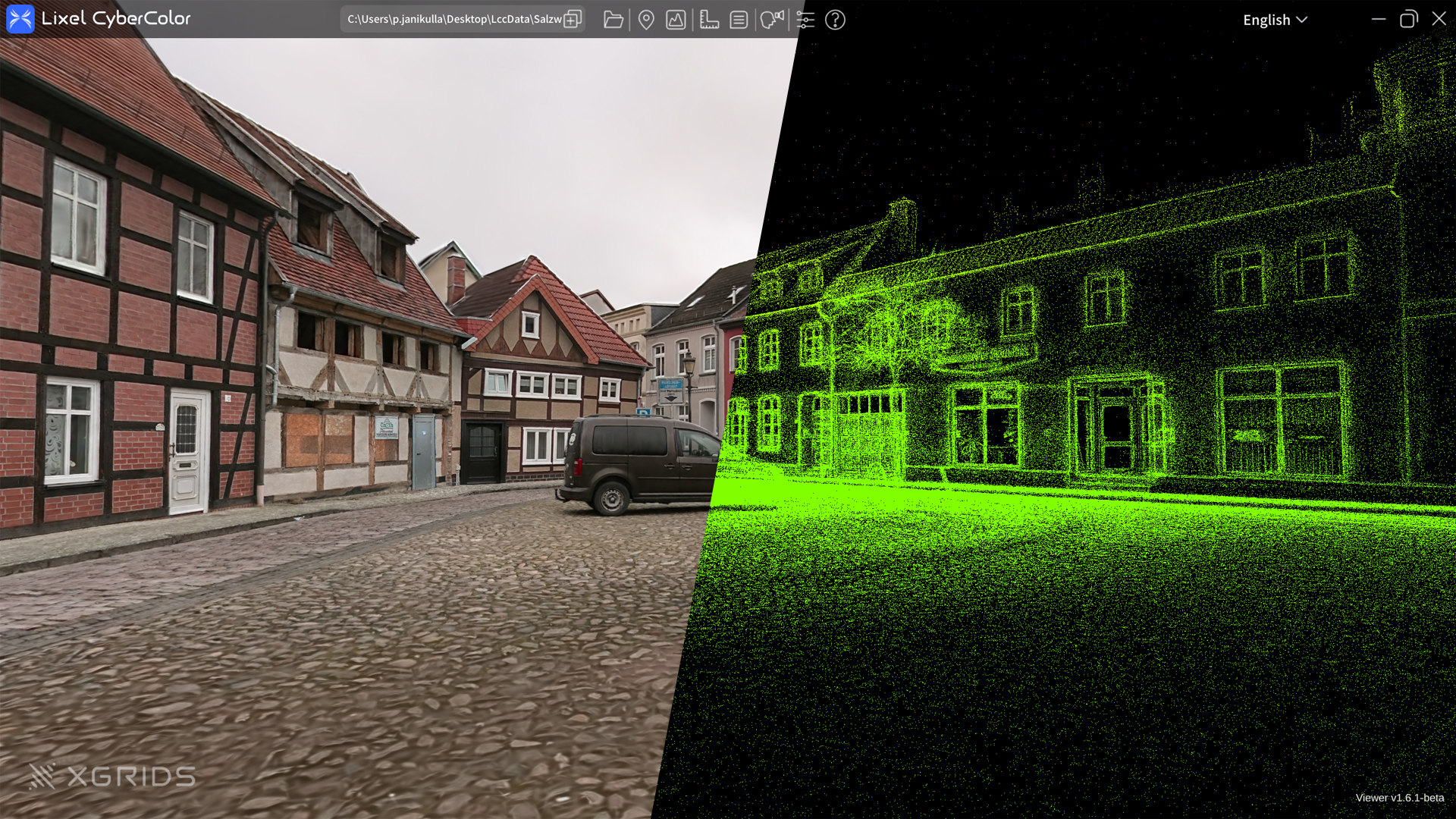
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) is a visualization technology that makes it possible to visualize large point clouds efficiently and in high quality. Unlike traditional methods that use point clouds or meshes, Gaussian Splatting represents each point of the cloud by a Gaussian distribution, allowing smoother and more realistic visualizations to be generated with significantly smaller amounts of data. This technique is widely used in surveying, CGI, VFX and even the gaming industry, allowing huge amounts of data to be processed and visualized more efficiently.
TitleHow is a Gaussian Splat scene created?
Gaussian splatting is a method for the efficient representation of point clouds, which is achieved by converting point data into so-called Gaussian kernels (splats). These Gaussian kernels represent the point clouds in a smooth and continuous form.
First, the 3D point coordinates of a point cloud are recorded, for example using a laser scanner or photogrammetric methods. In addition to the coordinates, each point is also given attributes such as color and normals. These points are then modeled as Gaussian distributions, with their shape adjusted by parameters such as extent and direction in order to precisely represent the point cloud.
The advantage lies in the smooth representation of surfaces and the saving of storage space, as fewer data points are used. The Gaussian kernels are rendered for visualization, which enables a detailed representation.
Gaussian splatting is particularly efficient for displaying large point clouds, such as those used in 3D surveying or in the CGI sector.
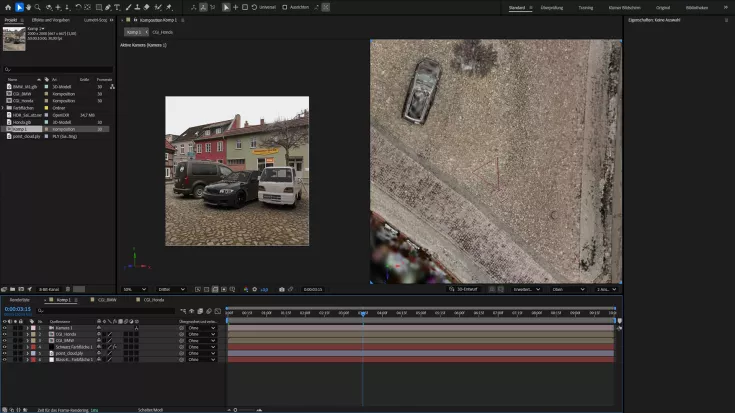
We use the LCC Studio software to process the Lixel K1 and L2 Pro scanners:
TitleMobile laser scanners and Gaussian splatting
The combination of mobile laser scanners and Gaussian splatting opens up completely new possibilities in 3D data acquisition. Mobile laser scanners using SLAM technology can quickly scan large areas and generate point clouds. Once these point clouds are available, the Gaussian splatting algorithm can be applied to efficiently visualize the captured data. Mobile capture combined with the detailed visualization of 3DGS allows surveyors to visualize construction projects or inspections even more vividly or to give the end customer a clear picture of the project situation.
TitleGaussian splatting - advantages for end customers
3D Gaussian splatting offers enormous advantages for end customers working in areas such as surveying, construction or inspection:
Small amount of data compared to meshes or point clouds
In contrast to conventional meshes or point clouds, which often require large storage capacities, a 3DGS scene requires significantly less storage space. This makes data storage and data exchange easier and more cost-effective.
Inspection of construction projects
For end customers in the construction industry, 3DGS enables fast and precise monitoring of construction projects. The efficient visualisation of point clouds allows progress or potential problems to be monitored and analysed in real time.
Fast evaluation and visualisation
The biggest advantage of 3DGS is its speed. End customers can immediately visualise and analyse the captured data and make decisions without having to wait for time-consuming post-processing.
TitleAreas of application for Gaussian splatting
Gaussian splatting in building surveying
Gaussian splatting is revolutionising the use of coloured point clouds in building surveying and other areas of geodesy. Large landscapes, buildings or infrastructures can be efficiently captured and visualised with maximum accuracy. Surveyors benefit from the fast data processing and realistic visualisation offered by Gaussian Splatting. This means that projects can be viewed as if they were on site and customers can be offered a better visualisation than with a point cloud.
- Clear visualisation for the customer
- Insertion of 3D models for refurbishments, for example
- Better project planning on site
Gaussian splatting in monument preservation
Gaussian splatting takes the visualisation possibilities in monument preservation to a new level. This technology enables historical buildings and cultural sites to be captured and visualised in great detail. 3DGS makes it possible to efficiently visualise complex surface structures, such as ornamentation and architectural details, without generating enormous amounts of data. This helps conservationists to create precise digital models for restoration and documentation purposes. At the same time, Gaussian Splatting allows realistic visualisation of the captured structures in virtual reality environments for immersive research or to simulate restoration measures.
- Detailed recording of historical buildings
- Efficient storage of large point cloud data
- Virtual simulation of restoration projects
Gaussian splatting in the CGI and VFX industry
In the CGI and VFX industry, 3DGS is increasingly used to create realistic 3D environments and effects. As 3DGS enables a more detailed representation of surfaces, 3D artists and designers can visualise large scenes with minimal effort. The ability to process point clouds efficiently not only saves time but also reduces the resources required, resulting in a significant improvement in the production process.
- Realistic, detailed environments
- Movement function
- Plugins for Nuke, Cinema4D, Davinci Resolve ...
Gaussian splatting in the gaming industry
The gaming industry also benefits from the efficiency and performance of Gaussian splatting. Game developers can create huge open-world games and realistic environments without massively increasing hardware requirements. 3DGS makes it possible to display highly complex landscapes with less computational effort, resulting in a smoother gaming experience. In addition, the real-time capability of Gaussian Splatting can further drive the development of immersive virtual reality games.
- Generation of collision data
- Rendering of large environments
- Interaction with the GS model